It is Cluster admins responsibility to setup and configure Rabbitmq Message Broker and Build Cluster Queue Worker.
Managing the Build Cluster Queue Worker
This page will cover how to setup RabbitMQ Message Broker and Build Cluster Queue Worker.
Overview
Build cluster feature can be enabled/disabled by multiBuildCluster feature flag or using environment variable. When enabled Screwdriver Queue Service will push build message to Rabbitmq exchange. Build message header will be set with routing key based on an active flag and weightage defined in buildClusters table. Rabbitmq exchange will route build message to queue based on routing key defined in message header and build message will be consumed and processed by Build Cluster Queue Worker. For build cluster stickiness, when first build is run for a pipeline, build cluster routing key will be added to pipeline annotations. Build cluster stickiness will not impact when a build cluster is taken offline for maintenance as builds will be automatically routed to next available build cluster.
Caution: Please give attention when creating buildCluster routing keys and be cautious or refrain updating routing key. Routing key is added to pipeline annotations for build cluster stickiness. So any updates to routing key, need to be cascaded to affected pipelines annotations and rabbitmq exchange bindings. Without this update, builds related to affected pipeline will error. Another option is to create a new build cluster and disable old build cluster. In this case builds will auto route to new build cluster without any updates, but please keep in mind build cluster stickiness will be lost.*
Retry queues
Build clusters can be setup with retry queues to verify pod status and stop any rogue builds with image pull errors or config errors.
This can be enabled by using an active flag. It has a default value set to true.
When this is used messages which do not return successful (pod status Running) after first processing will be sent to the retry queue, where it will be delayed and retried based on configuration until it gets the successful status or exhausts the reprocessing limit.
Setup Build Cluster
Cluster admin should create build cluster using buildclusters API
{
"name": "ClusterA",
"description": "Build cluster to process ClusterA builds",
"scmOrganizations": [
"screwdriver-cd"
],
"isActive": true,
"managedByScrewdriver": true,
"maintainer": "foo@bar.com",
"weightage": 100
}
- name should match the queue and routing key defined in rabbitmq configuration.
- set
managedByScrewdrivertotrue, if build cluster is managed by internal Screwdriver team. - set
isActivetotrueorfalseto turn on/off a build cluster. - set weightage 100 if you have single build cluster and for more than one cluster, distribute the weightage accordingly.
Caution: Build cluster scmContext is derived from API token of specific scm. In order to create build clusters with same name for multiple scm, repeat post /v4/buildClusters api for each scm account.
Install RabbitMQ Message Broker
As a prerequisite go through Downloading and Installing Rabbitmq and Rabbitmq Tutorials documentation.
Screwdriver uses helm charts to install Rabbitmq high availability version: 3.7.28 Erlang: 22.3.4.7 in Kubernetes cluster.
Please note that this helm chart is deprecated and for new installation refer bitnami helm charts.
Rabbitmq helm chart values.tmpl file for your reference. Update and use it per your environment specifications.
## RabbitMQ application credentials
## Ref: http://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
## Assumption: CPU:1; Memory:2Gi
rabbitmqUsername: sdadmin
rabbitmqPassword: replace_password
## RabbitMQ Management user used for health checks
managementUsername: sdmgmt
managementPassword: replace_password
## Place any additional key/value configuration to add to rabbitmq.conf
## Ref: https://www.rabbitmq.com/configure.html#config-items
extraConfig:
disk_free_limit.absolute = 5GB
## Place any additional plugins to enable in /etc/rabbitmq/enabled_plugins
## Ref: https://www.rabbitmq.com/plugins.html
extraPlugins: |
rabbitmq_shovel,
rabbitmq_shovel_management,
rabbitmq_federation,
rabbitmq_federation_management
definitions:
users: |-
vhosts: |-
parameters: |-
permissions: |-
queues: |-
exchanges: |-
bindings: |-
policies: |-
## RabbitMQ default VirtualHost
## Ref: https://www.rabbitmq.com/vhosts.html
##
rabbitmqVhost: "/"
## Erlang cookie to determine whether different nodes are allowed to communicate with each other
## Ref: https://www.rabbitmq.com/clustering.html
##
rabbitmqErlangCookie: replace_erlang_cookie
## RabbitMQ Memory high watermark
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/memory.html
##
rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark: 1024MiB
rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermarkType: absolute
## EPMD port for peer discovery service used by RabbitMQ nodes and CLI tools
## Ref: https://www.rabbitmq.com/clustering.html
##
rabbitmqEpmdPort: 4369
## Node port
rabbitmqNodePort: 5672
## Manager port
rabbitmqManagerPort: 15672
## Set to true to precompile parts of RabbitMQ with HiPE, a just-in-time
## compiler for Erlang. This will increase server throughput at the cost of
## increased startup time. You might see 20-50% better performance at the cost
## of a few minutes delay at startup. ## Rabbitmq crashes when this settings
## is enabled
rabbitmqHipeCompile: false
## SSL certificates
## Red: http://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html
rabbitmqCert:
enabled: true
# Specifies an existing secret to be used for SSL Certs
existingSecret: replace_tls_cert
## Create a new secret using these values
cacertfile: |
certfile: |
keyfile: |
## Authentication mechanism
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/authentication.html
rabbitmqAuth:
enabled: false
config: |
# auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.3 = EXTERNAL
## Authentication backend
## Ref: https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-auth-backend-http
rabbitmqAuthHTTP:
enabled: false
config: |
# auth_backends.1 = http
# auth_http.user_path = http://some-server/auth/user
# auth_http.vhost_path = http://some-server/auth/vhost
# auth_http.resource_path = http://some-server/auth/resource
# auth_http.topic_path = http://some-server/auth/topic
## LDAP Plugin
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/ldap.html
rabbitmqLDAPPlugin:
enabled: false
## LDAP configuration:
config: |
# auth_backends.1 = ldap
# auth_ldap.servers.1 = my-ldap-server
# auth_ldap.user_dn_pattern = cn=${username},ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
# auth_ldap.use_ssl = false
# auth_ldap.port = 389
# auth_ldap.log = false
## MQTT Plugin
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/mqtt.html
rabbitmqMQTTPlugin:
enabled: false
## MQTT configuration:
config: |
# mqtt.default_user =
# mqtt.default_pass =
# mqtt.allow_anonymous = true
## Web MQTT Plugin
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/web-mqtt.html
rabbitmqWebMQTTPlugin:
enabled: false
## Web MQTT configuration:
config: |
# web_mqtt.ssl.port = 12345
# web_mqtt.ssl.backlog = 1024
# web_mqtt.ssl.certfile = /etc/cert/cacert.pem
# web_mqtt.ssl.keyfile = /etc/cert/cert.pem
# web_mqtt.ssl.cacertfile = /etc/cert/key.pem
# web_mqtt.ssl.password =
## STOMP Plugin
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/stomp.html
rabbitmqSTOMPPlugin:
enabled: false
## STOMP configuration:
config: |
# stomp.default_user =
# stomp.default_pass =
## Web STOMP Plugin
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/web-stomp.html
rabbitmqWebSTOMPPlugin:
enabled: false
## Web STOMP configuration:
config: |
# web_stomp.ws_frame = binary
# web_stomp.cowboy_opts.max_keepalive = 10
## AMQPS support
## Ref: http://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html
rabbitmqAmqpsSupport:
enabled: true
# NodePort
amqpsNodePort: 5671
# SSL configuration
config: |
listeners.ssl.default = 5671
ssl_options.cacertfile = /etc/cert/tls.crt
ssl_options.certfile = /etc/cert/tls.crt
ssl_options.keyfile = /etc/cert/tls.key
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = false
## Number of replicas
replicaCount: 2
image:
repository: rabbitmq
tag: 3.7-alpine
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Optionally specify an array of imagePullSecrets.
## Secrets must be manually created in the namespace.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/
##
# pullSecrets:
# - myRegistrKeySecretName
## Duration in seconds the pod needs to terminate gracefully
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
service:
annotations: {}
clusterIP: None
## List of IP addresses at which the service is available
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/services/#external-ips
##
externalIPs: []
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
type: ClusterIP
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
## Statefulsets rolling update update strategy
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/stateful-application/basic-stateful-set/#rolling-update
##
updateStrategy: RollingUpdate
## Statefulsets Pod Priority
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
## priorityClassName: ""
## We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as
## a conscious choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on
## environments with little resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to
## specify resources, uncomment the following lines, adjust them as necessary,
## and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
## If you decide to set the memory limit, make sure to also change the
## rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark following the formula:
## rabbitmqMemoryHighWatermark = 0.4 * resources.limits.memory
##
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 2Gi
initContainer:
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 100mm
# memory: 128Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100mm
# memory: 128Mi
## Data Persistency
persistentVolume:
enabled: true
## If defined, storageClassName: <storageClass>
## If set to "-", storageClassName: "", which disables dynamic provisioning
## If undefined (the default) or set to null, no storageClassName spec is
## set, choosing the default provisioner. (gp2 on AWS, standard on
## GKE, AWS & OpenStack)
##
storageClass: "enc-gp2"
name: data
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
size: 100Gi
annotations: {}
## Node labels for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector
##
nodeSelector: {}
## Node tolerations for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#taints-and-tolerations-beta-feature
##
tolerations: []
## Extra Annotations to be added to pod
podAnnotations: {}
## Pod affinity
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
podAntiAffinity: soft
## Create default configMap
##
existingConfigMap: false
## Add additional labels to all resources
##
extraLabels: {}
## Role Based Access
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/admin/authorization/rbac/
##
rbac:
create: false
## Service Account
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/admin/service-accounts-admin/
##
serviceAccount:
create: false
## The name of the ServiceAccount to use.
## If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
# name:
ingress:
## Set to true to enable ingress record generation
enabled: true
path: /
## The list of hostnames to be covered with this ingress record.
## Most likely this will be just one host, but in the event more hosts are needed, this is an array
hostName: replace_host_name
## Set this to true in order to enable TLS on the ingress record
tls: true
## If TLS is set to true, you must declare what secret will store the key/certificate for TLS
tlsSecret: replace_tls_cert
## Ingress annotations done as key:value pairs
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 120
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 6
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 6
initialDelaySeconds: 20
timeoutSeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 5
# Specifies an existing secret to be used for RMQ password and Erlang Cookie
existingSecret: ""
prometheus:
## Configures Prometheus Exporter to expose and scrape stats.
exporter:
enabled: true
env: {}
image:
repository: kbudde/rabbitmq-exporter
tag: v0.28.0
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Port Prometheus scrapes for metrics
port: 9090
## Comma-separated list of extended scraping capabilities supported by the target RabbitMQ server
capabilities: "bert,no_sort"
## Allow overriding of container resources
resources: {}
# limits:
# cpu: 200m
# memory: 1Gi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 100Mi
## Prometheus is using Operator. Setting to true will create Operator specific resources like ServiceMonitors and Alerts
operator:
## Are you using Prometheus Operator? [Blog Post](https://coreos.com/blog/the-prometheus-operator.html)
enabled: false
## Configures Alerts, which will be setup via Prometheus Operator / ConfigMaps.
alerts:
## Prometheus exporter must be enabled as well
enabled: false
## Selector must be configured to match Prometheus Install, defaulting to whats done by Prometheus Operator
## See [CoreOS Prometheus Chart](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/tree/master/helm)
selector:
role: alert-rules
labels: {}
serviceMonitor:
## Interval at which Prometheus scrapes RabbitMQ Exporter
interval: 10s
# Namespace Prometheus is installed in
namespace: monitoring
## Defaults to whats used if you follow CoreOS [Prometheus Install Instructions](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/tree/master/helm#tldr)
## [Prometheus Selector Label](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/blob/master/helm/prometheus/templates/prometheus.yaml#L65)
## [Kube Prometheus Selector Label](https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/blob/master/helm/kube-prometheus/values.yaml#L298)
selector:
prometheus: kube-prometheus
Rabbitmq Configuration
Configure Rabbitmq definitions using Rabbitmq admin UI manually or use Import definitions.
{
"rabbit_version": "3.7.24",
"users": [
{
"name": "sdrw",
"password_hash": "",
"hashing_algorithm": "rabbit_password_hashing_sha256",
"tags": ""
},
{
"name": "sdadmin",
"password_hash": "",
"hashing_algorithm": "rabbit_password_hashing_sha256",
"tags": "administrator"
},
{
"name": "sdro",
"password_hash": "",
"hashing_algorithm": "rabbit_password_hashing_sha256",
"tags": ""
}
],
"vhosts": [
{
"name": "/"
},
{
"name": "screwdriver"
}
],
"permissions": [
{
"user": "sdro",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"configure": "",
"write": "",
"read": "^(build|clusterA|clusterB)$"
},
{
"user": "sdrw",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"configure": "^(build|clusterA|ClusterARetry|ClusterB|ClusterBRetry)$",
"write": "^(build|clusterA|ClusterARetry|ClusterB|ClusterBRetry)$",
"read": "^(build|clusterA|ClusterARetry|ClusterB|ClusterBRetry)$"
},
{
"user": "sdadmin",
"vhost": "/",
"configure": ".*",
"write": ".*",
"read": ".*"
},
{
"user": "sdadmin",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"configure": ".*",
"write": ".*",
"read": ".*"
}
],
"topic_permissions": [],
"parameters": [
{
"value": {
"max-connections": 50
},
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"component": "vhost-limits",
"name": "limits"
}
],
"global_parameters": [
{
"name": "cluster_name",
"value": "rabbit@rabbitmq-ha-0.rabbitmq-ha-discovery.screwdriver.svc.cluster.local"
}
],
"policies": [
{
"vhost": "/",
"name": "ha-root",
"pattern": "",
"apply-to": "all",
"definition": {
"ha-mode": "exactly",
"ha-params": 2,
"ha-sync-mode": "automatic"
},
"priority": 0
},
{
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"name": "ha-screwdriver",
"pattern": "^(build|ClusterA|ClusterAdlr|ClusterARetry|ClusterARetrydlr|ClusterB|ClusterBdlr|ClusterBRetry|ClusterBRetrydlr|default)$",
"apply-to": "all",
"definition": {
"ha-mode": "exactly",
"ha-params": 2,
"ha-sync-batch-size": 1,
"ha-sync-mode": "automatic"
},
"priority": 0
},
{
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"name": "message-delay",
"pattern": "^(ClusterARetrydlr|ClusterBRetrydlr)$",
"apply-to": "queues",
"definition": {
"message-ttl": 60000
},
"priority": 1
}
],
"queues": [
{
"name": "ClusterB",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterBdlr",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 28800000
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterAdlr",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterA",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 5000
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterBdlr",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterB",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 5000
}
},
{
"name": "default",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-message-ttl": 1800000,
"x-queue-mode": "lazy"
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterA",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterAdlr",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 28800000
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterARetry",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterARetrydlr",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 28800000
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterARetrydlr",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterARetry",
"x-max-priority": 2
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterBRetry",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterBRetrydlr",
"x-max-priority": 2,
"x-message-ttl": 28800000
}
},
{
"name": "ClusterBRetrydlr",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"arguments": {
"x-dead-letter-exchange": "build",
"x-dead-letter-routing-key": "ClusterBRetry",
"x-max-priority": 2
}
}
],
"exchanges": [
{
"name": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"type": "topic",
"durable": true,
"auto_delete": false,
"internal": false,
"arguments": {}
}
],
"bindings": [
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "default",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterB",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterB",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterBdlr",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterBdlr",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterA",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterA",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterAdlr",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterAdlr",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterARetry",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterARetry",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterBRetry",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterBRetry",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterARetrydlr",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterARetrydlr",
"arguments": {}
},
{
"source": "build",
"vhost": "screwdriver",
"destination": "ClusterBRetrydlr",
"destination_type": "queue",
"routing_key": "ClusterBRetrydlr",
"arguments": {}
}
]
}
Note:
- Queues suffixed with
dlrare deadletter queues. We use the built-in rabbitmq deadletter queue mechanism for a retry with delay in case of errors. Deadletter queues are used in case of any error in consuming the message and pushing to Kubernetes cluster for build processing. When a message isnack'dit goes to dlr queues via deadletter routing key configuration and re-pushed to actual queue after a delay of 5s (per below configuration). buildis exchange.ClusterAandClusterBare queues.ClusterAdlrandClusterBdlrare deadletter queues forClusterAandClusterBqueues respectively.ClusterARetryandClusterBRetryare retry queues forClusterAandClusterBqueues respectively which will receive messages if build pod status is not successful for start jobs.ClusterARetrydlrandClusterBRetrydlrare deadletter queues forClusterARetryandClusterBRetryqueues respectively which will delay messages for 60s before re-enqueing them for processing.
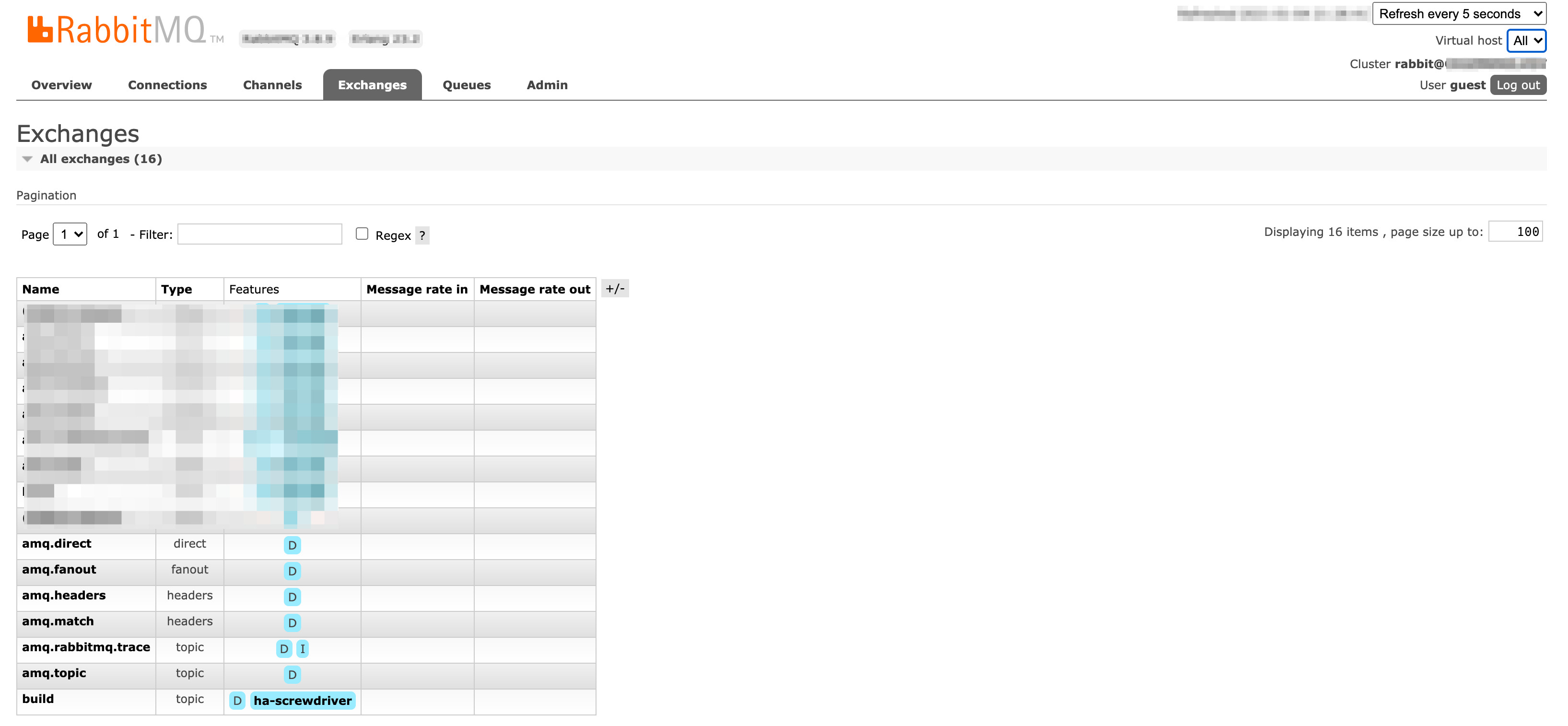
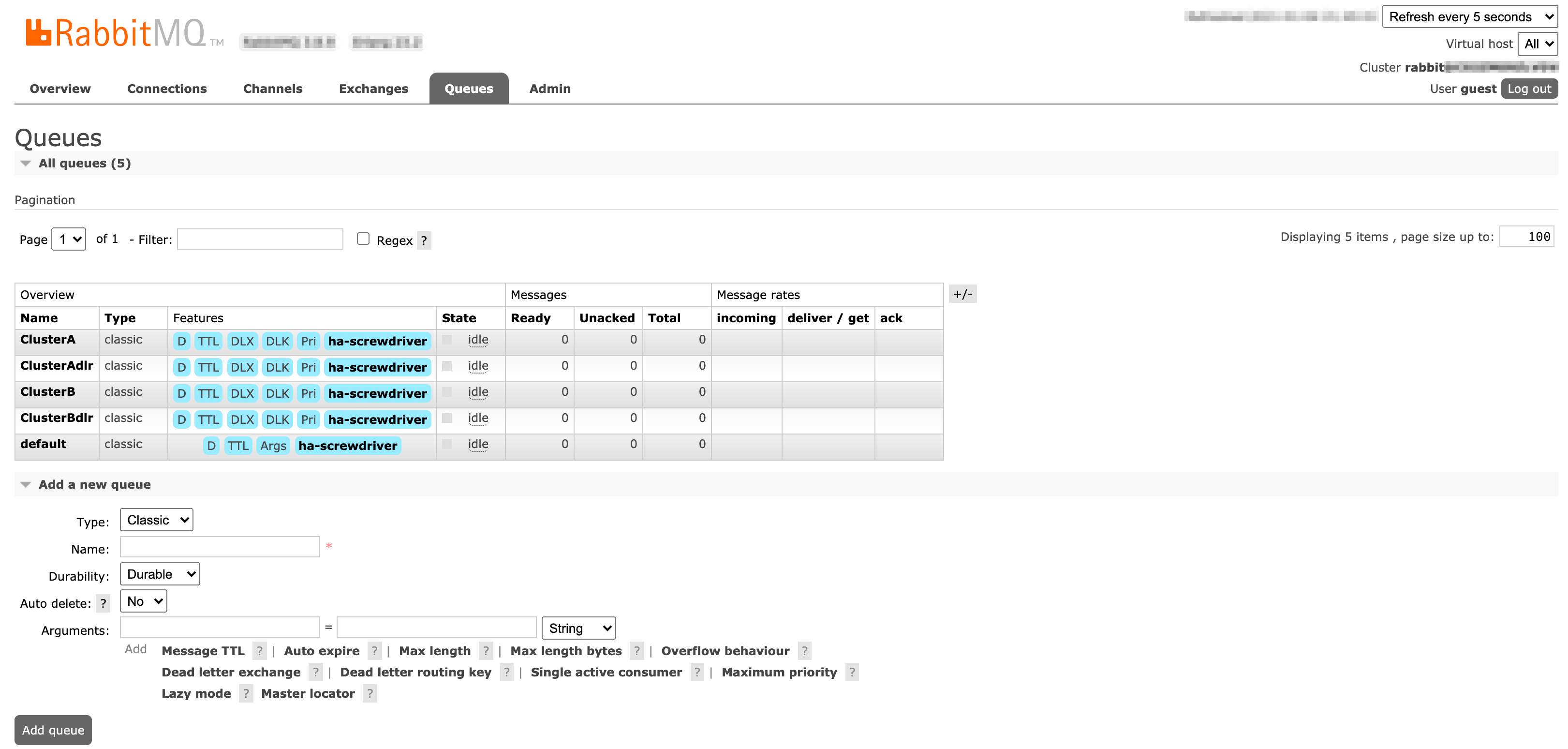
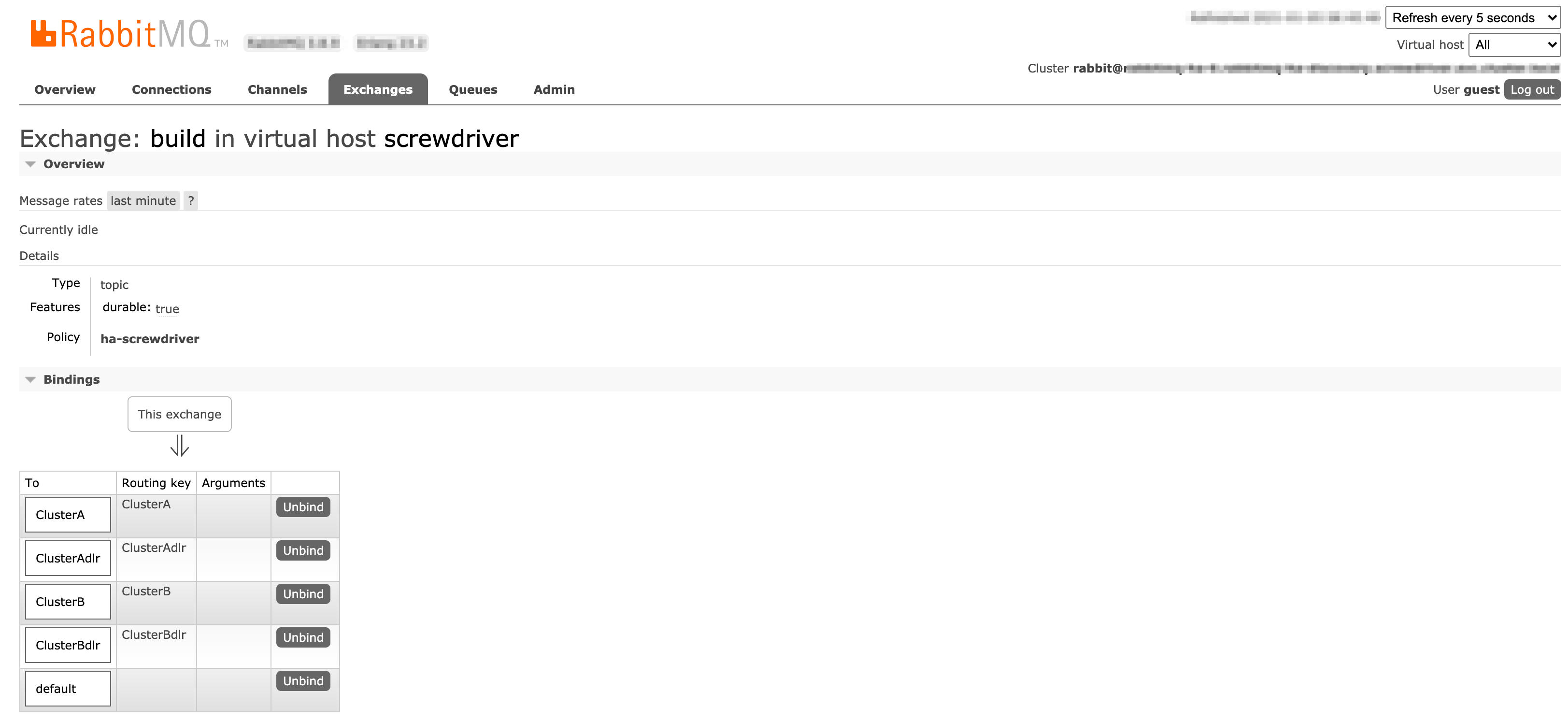
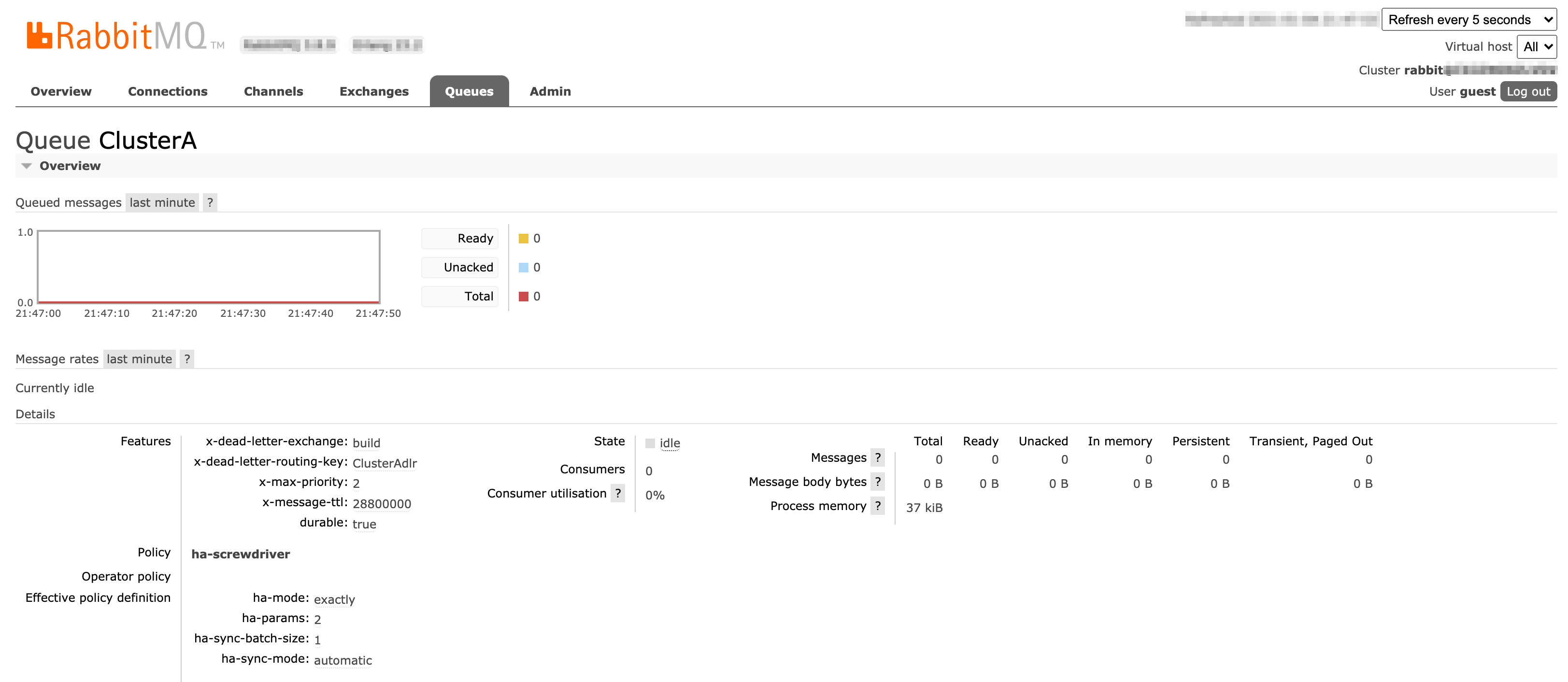
User Interface
Screenshots of Exchanges, Queues page from Rabbitmq admin UI
Exchanges:
Queues:
Exchange (build) configuration:
ClusterA queue configuration:
ClusterAdlr queue configuration:
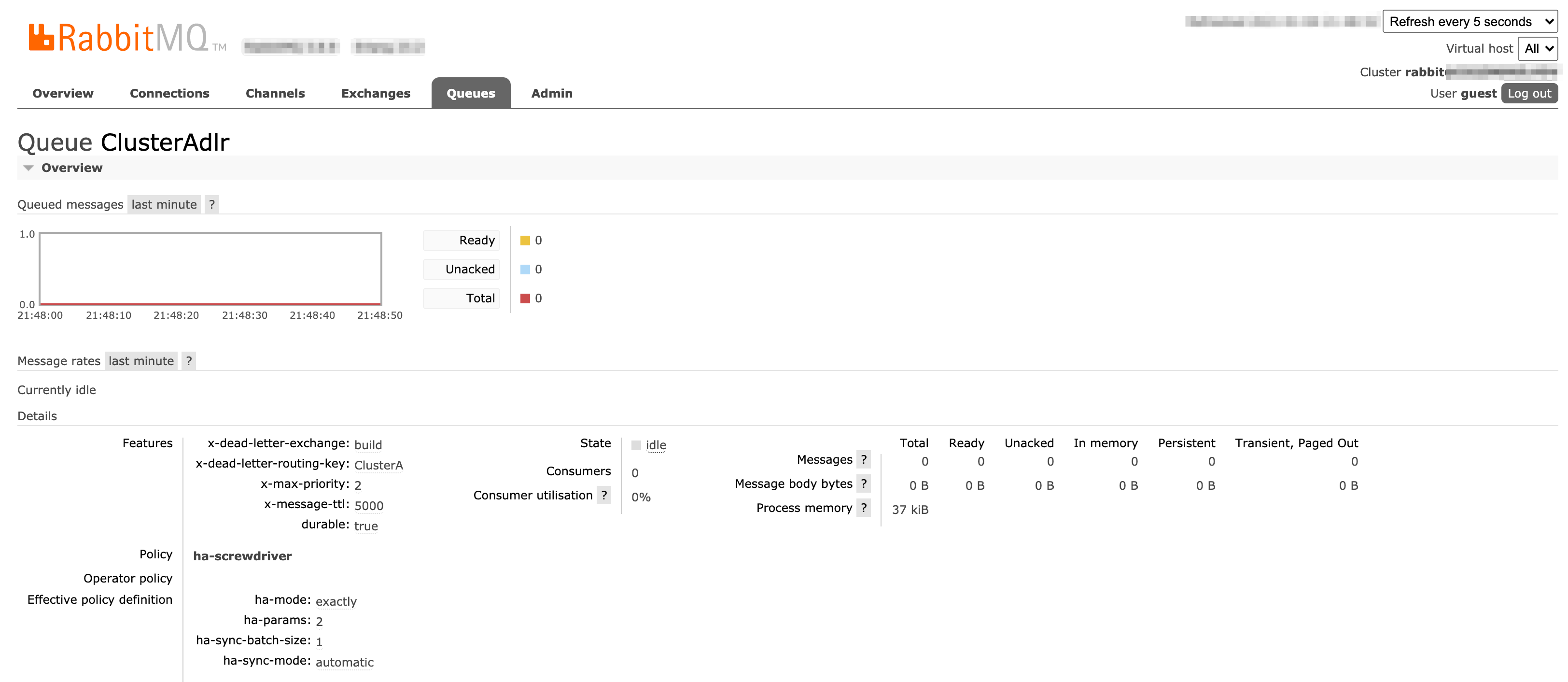
ClusterARetry queue configuration:
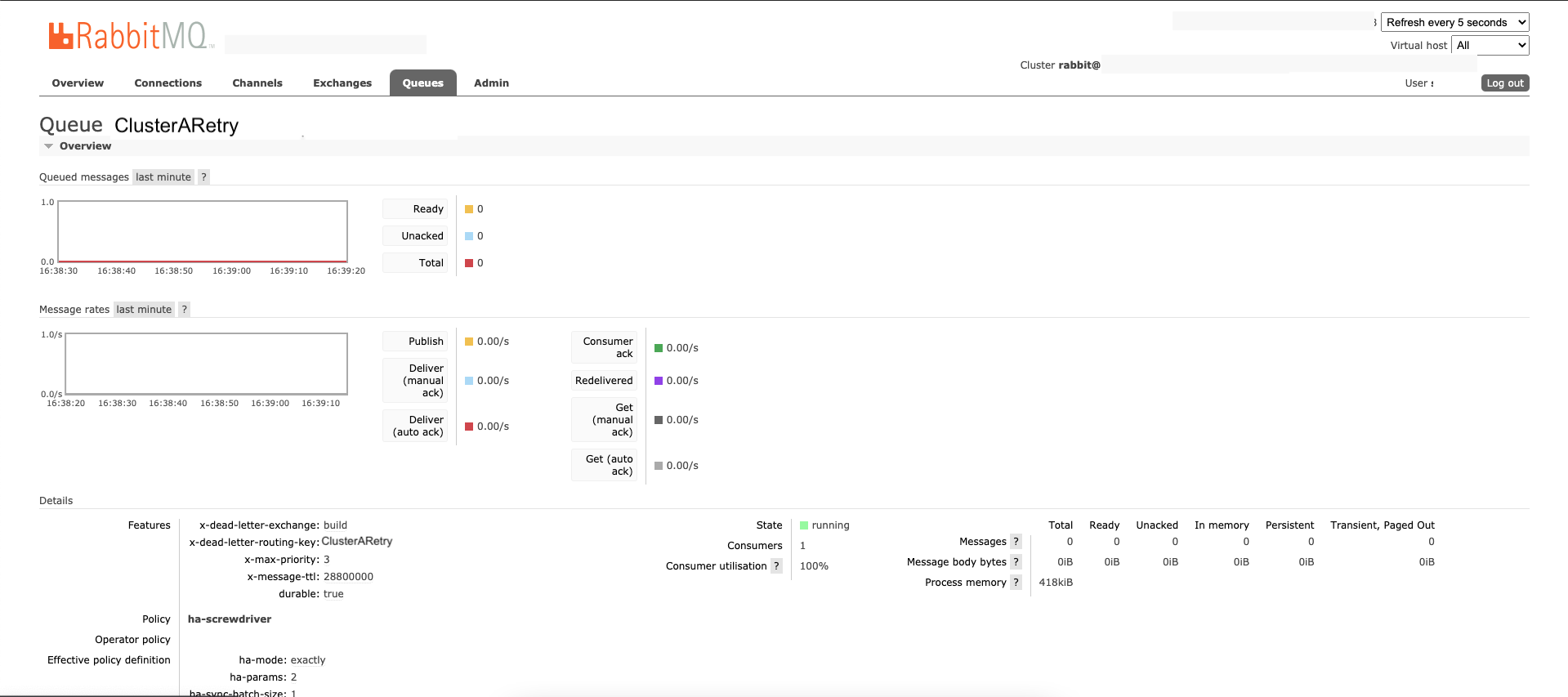
ClusterARetrydlr queue configuration:
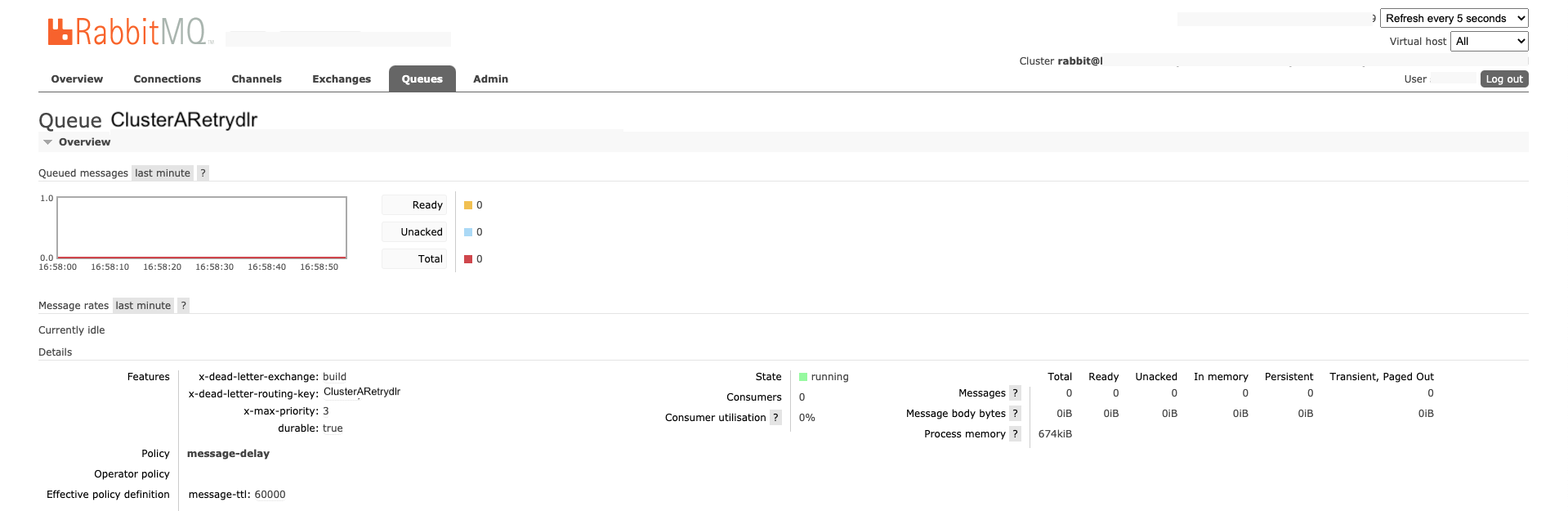
Refer to Connections and Channels page to check connections with a username established by Screwdriver Queue Service (Producer) and Build Cluster Queue Worker (Consumer).
To get rabbitmq message delivery and acknowledgement rates refer to Message rates of each queue in Queues page.
Setup Build Cluster Queue Worker
Please refer to
- Docker Image for setup and installation. Our images are tagged with the version (eg.
v1.2.3) as well as a floating taglatestandstable. Most installations should be usingstableor the fixed version tags. - Repository for implementation.
Configure Build Cluster Queue Worker
RabbitMQ
Build Cluster Queue Worker already defaults all configuration in rabbitmq section, but you can override defaults using environment variables in rabbitmq section.
| Key | environment variable | Description | |:———————-|:———————|:——————————————————————————————————| | protocol | RABBITMQ_PROTOCOL | Protocol to connect to rabbitmq. Use amqp for non-ssl and amqps for ssl. Default: amqp | | username | RABBITMQ_USERNAME | User to connect and authorized to consume from rabbitmq queues | | password | RABBITMQ_PASSWORD | password | | host | RABBITMQ_HOST | Rabbitmq cluster hostname. Default: 127.0.0.1 | | port | RABBITMQ_PORT | Rabbitmq port. Default: 5672 | | vhost | RABBITMQ_VIRTUAL_HOST | Virtual host for queues. Default: /screwdriver | | connectOptions | RABBITMQ_CONNECT_OPTIONS | options to configure hearbeat check and reconnect in time in case of broken connections. Default: ‘{ “json”: true, “heartbeatIntervalInSeconds”: 20, “reconnectTimeInSeconds”: 30 }’ | | queue | RABBITMQ_QUEUE | queue to consume from | | prefetchCount | RABBITMQ_PREFETCH_COUNT | used to specify how many messages are sent at the same time. Default: “20” | | messageReprocessLimit | RABBITMQ_MSG_REPROCESS_LIMIT | maximum number of retries in case of errors. Default: “3”. If this is set > 0 build cluster queue worker will expect deadletter queue to retry. | | retryQueue | RABBITMQ_RETRYQUEUE | Queue name of the retry queue. | | retryQueueEnabled | RABBITMQ_RETRYQUEUE_ENABLED | retry queue enable/disable flag. | | exchange | RABBITMQ_EXCHANGE | Exchange / router name for rabbitmq to publish message. |
Executors
Executor configuration settings are exactly same as the settings configuration for API.
Ecosystem
Cache settigs are used for queue messages which deals with cleaning up disk based cache.
| Key | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ECOSYSTEM_UI | https://cd.screwdriver.cd | URL for the User Interface |
| ECOSYSTEM_STORE | https://store.screwdriver.cd | URL for the Artifact Store |
| ECOSYSTEM_API | https://api.screwdriver.cd | URL for API |
| ECOSYSTEM_PUSHGATEWAY_URL | ”” | URL for Prometheus Push Gateway |
| CACHE_STRATEGY | “s3” | Buld cache strategy |
| CACHE_PATH | ”/” | Disk based cache setting. |
| CACHE_COMPRESS | false | Disk based cache setting. |
| CACHE_MD5CHECK | false | Disk based cache setting. |
| CACHE_MAX_SIZE_MB | 0 | Disk based cache setting. |
| CACHE_MAX_GO_THREADS | 10000 | Disk based cache setting. |
HTTP
This is used for liveness checks. See
Build Cluster Schema Definition
-
name and scmContext fields form a unique constraint for a buildcluster.